Cell Theory
- All living things are made up of cells
- Cells are the smallest working units of all living things
- All cells come from pre-existing cells through cell division
Definition
A cell is the smallest unit that is capable of performing life functions
Examples
Amoeba proteus
Red blood cell etc...
Types
- Prokaryotic
- Eukaryotic
Prokaryotic
- Do not have organelles surrounded by membranes
- Few internal structure
- One-celled organisms (bacteria)
Eukaryotic
 |
| Animal |
- Contain organelles surrounded by membranes
- Most living organisms eg. plant, animal, fungi
 |
| http://waynesword.palomar.edu/images/plant3.gif (Not accurate) |
Cell Wall
- Most commonly found in plant cells & bacteria
- Surrounds the cell membrane
- Rigid structure that maintains the shape, supports & protects cells
- Permeable to small molecules & small proteins only
Cell Membrane
- Selectively permeable/partially permeable membrane of cell that controls movement of substances in and out of the cell
Nucleus
- Contain chromatins that control cell activities
- Chromatins contain DNA which is the genetic material
- DNA contain instructions for traits & characteristics & carry out the cell's function
- Separated from cytoplasm by nuclues membrane
Cytoplasm
- Gel-like mixture
- Surrounded by cell membrane
- Contains organelles (nucleus)
Mitochondria
- Refer to the "powerhouse" of the cell
- The food we eat is transformed into energy (ATP) for the cells & our bodies
Endoplasmic Reticulum
- An interconnected network of tubes and vesicles
- Synthesis of proteins, fats, steroid
- Transports materials around in cell
- Smooth type: lacks ribosomes
- Rough type" ribosomes embedded in surface
Ribosomes
- Each cells contain thousands
- Make proteins
- Found on endoplasmic reticulum & floating throughout the cell
Golgi Bodies/ Apparatus
- Work closely with ER
- Primary function is to process and package complex molecules such as proteins and fats that are made by the cell
- Brings these products to the surface of the cell where they can be secreted
- Other secretions include hormones, antibodies & enzymes
Lysosome
- Contain digestive enzymes
- Digest excess or worn-put organelles, food particles and engulf bacteria or viruses
- Also help repair worn-out plasma membrane
- They also provide sugars, amino acids and bases which are the foundation of macromolecules
- Cell breaks down if lysosome explodes
Vacuoles
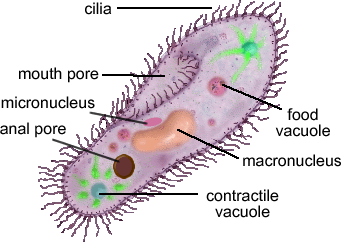 |
| http://www.biologycorner.com/resources/paramecium.gif |
- Membrane-bound sacs for storage, digestion, and waste removal
- Central large vacuole-help plant cells maintain shape
- Food vacuoles: formed by phagocytes
- Contractile vacuoles (in freshwater protists): pump excess water out of the cell-------------->not in syllabus!
Chloroplasts (Absent in Animals)
- Usually found in plant cells
- Contain green chlorophyll
- Where photosynthesis takes place
- Converts light energy into chemical energy in glucose
Differences in Plants & Animals:
- Plant cell has cell wall while animal doesn't
- Plant cells has a large vacuole while animal cells has numeral small cells
- Plant cell has a fixed shape while animal cell has an irregular shape
- Plant cell has chloroplasts but animal cell doesn't

No comments:
Post a Comment
Comments Very Much Appreciated